
Most Common Problems with Mitsubishi Air Conditioner
If you’re having problems with your Mitsubishi air conditioner, it won’t always mean that you need to fix it or shop for a replacement because a majority of these problems can be solved easily. In this Mitsubishi Air Conditioning Troubleshooting Guide, we’ll cover:
- Causes of 12 common Mitsubishi AC and Mitsubishi controller problems
- How to resolve some simple issues with your Mitsubishi AC unit
- When you should call a qualified professional for help
- How to reset your Mitsubishi AC unit
- The most common Mitsubishi error codes
- Where to get more information on your specific Mitsubishi AC model
Our troubleshooting guide will walk you through each of the sections mentioned above and help you to deduce any underlying issues with your Mitsubishi AC system.
Get a Free Quote From Your Local Mitsubishi Air Conditioning Expert
*Offer to be presented at point of booking or sale.
Troubleshooting Manual for Mitsubishi Air Conditioning
Here are some of the most common problems you may experience with a Mitsubishi air conditioner.
Mitsubishi Air Conditioner Not Turning On
If your Mitsubishi air conditioner not turning on is the problem you’re facing, it could indicate a tripped circuit breaker.
Take a look at the circuit breaker (you can find it in your metre box) and see if the air conditioner is turned on. If the trip has gone off, simply switch it back on again.
If the air conditioner keeps tripping the circuit breaker or if there’s a problem with your isolation switch—for example, if it’s too difficult to move or it’s getting stuck—you’ll want to call a qualified AC technician for help.
Mitsubishi Air Conditioner Keeps Turning On and Off
There are several reasons for this, such as a faulty timer, a problem with the compressor, or a condenser issue.
A faulty timer may cause your air conditioner to shut down randomly. Try changing the setting on your timer to see if the problem goes away. If the issue persists, you may have a broken timer on your hands.
In this case, you’ll need to call a technician to replace your timer.
Problems with your Mitsubishi air conditioner’s compressor or condenser can cause it to turn off and on randomly. These are two complex problems that you shouldn’t attempt to fix on your own — call an AC expert instead.
Mitsubishi Air Conditioner Won’t Turn Off
A few things can cause your Mitsubishi air conditioner to not turn off like the fan limit not being set to “auto”, the temperature setting being too low, or dirty filters.
When the fan limit is set to “on” instead of “auto”, the fan will continue to run regardless of the settings on your thermostat. To fix this issue, simply press the fan button on the control panel until the word “auto” shows on the screen.
When the temperature setting is too low, the air conditioner will continue to work without shutting off until it reaches the set temperature. This may take longer when your indoor environment is too hot and humid.
Dirty filters restrict the airflow, and this will make it harder for the AC to cool your interiors until it reaches the set temperature. Also, the AC will stay on longer to reach the desired temperature. To fix this issue, clean the filters and continue to clean them at least once every three months.
If your Mitsubishi air conditioner not turning on is a problem that persists even after following the above suggestions, give our Alliance Experts a call for further diagnosis.
Mitsubishi Air Conditioner is Not Cooling
There can be many reasons why your Mitsubishi air conditioner isn’t cooling like it should. These include blocked filters, low refrigerant, or a faulty component.
Blocked filters are a common occurrence in most air conditioners. After years of operation, an air conditioner’s filters will start to accumulate dust, and this will block the airflow, affecting cooling. In this case, all you need to do is clean them out and your AC will start working as normal.
Low refrigerant is usually caused by the air conditioner refrigerant leaking out o ver time. This issue can be fixed by replacing the refrigerant. However, you should leave this task to a professional technician.
Faulty components, such as a faulty compressor, fan, or electronic control board may also affect your air conditioner’s cooling capabilities. These problems are difficult for an untrained person to fix, so you should call an AC technician instead.
Mitsubishi Air Conditioner Not Blowing Air or Has Limited Airflow
This could be the result of dirty filters or a faulty motor damper, which is a valve that controls the airflow.
Cleaning out dirty filters may restore the airflow immediately. A faulty motor damper, however, may need to be replaced—but this should be done by a professional.
Mitsubishi Air Conditioner Blowing Warm Air Instead of Cold Air
A few reasons for this include the thermostat being set to “heat”, the outdoor unit having lost power, or the air conditioner being low on refrigerant.
If your Mitsubishi air conditioner model comes with a heating option, check and see if the thermostat is set to “heat”. If it is, just switch it back to “cool” and your AC should start cooling again as normal.
If the outdoor unit stops working, your air conditioner’s indoor unit may start blowing warm air into your home. Check your circuit breaker to see if there’s a blown fuse or a tripped switch—these could be the reasons for your outdoor unit losing power.
Low refrigerant levels will also lead to your AC blowing warm air as it isn’t able to cool the air beforehand. In this case, refilling the refrigerant may solve the problem. Be warned, however, as this chemical is toxic to people and pets, so always let a professional handle this for you.
However, as this chemical is toxic to people and pets, so always let a professional handle this for you.
Mitsubishi Air Conditioner Heating Mode Not Working
This could happen when you haven’t set the AC to heat mode or the filter is clogged.
Check your thermostat and see if it’s set to heat mode. If it isn’t, simply turn on heat mode and avoid setting it to auto mode.
A clogged filter can be resolved with a thorough cleaning which should be done at least once every few months to prevent it from getting clogged again in the future.
Mitsubishi Air Conditioner is Leaking Water
A leaking air conditioner may be a sign of the drain pipe being clogged.
This usually happens when mildew, dirt, and fungus form inside the drain pump and obstruct the flow of drain water. Simply clean out the block to allow the water to flow again.
Sometimes, a leak may indicate a damaged drain pipe; in this case, ask a professional to replace the pipe.
Mitsubishi Air Conditioner is Making Strange Noises
A noisy air conditioner may be a sign of loose components, a faulty compressor, or damaged isolation feet.
These problems can be too complicated for an untrained person to fix. Instead, you may want to call a technician to resolve the problem.
Mitsubishi Air Conditioner Swing Not Working
First, check and see if your AC is set in swing mode. If it is still not working, visually inspect the swings with a flashlight and check if there’s any foreign object jamming the swings and remove it carefully with a flat screwdriver.
If the swings are still not working, this could mean there is a problem with the swing motors, which is a far more difficult issue to resolve on your own.
Mitsubishi AC Controller Troubleshooting Manual
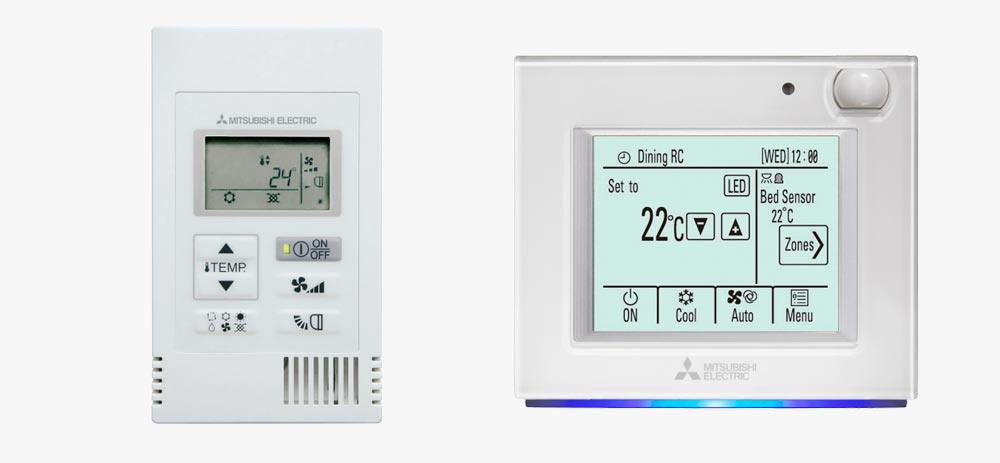

If your Mitsubishi air conditioner controller has an issue, applying one of the quick fixes below might help get it back up and running in no time.
Mitsubishi Control Board Not Turning On or is Showing a Blank Screen
This may indicate that you need to replace the batteries. Simply put in some fresh batteries and see if it turns on again. If it doesn’t, there could be a problem with the screen or the Control Board itself, in which case you may need to call a professional to repair it.
Mitsubishi AC Remote Control Not Turning On
Your Mitsubishi AC Remote Controller may need new batteries. Simply replace the batteries and see if it works. If it doesn’t, contact the manufacturer for a replacement controller.
Mitsubishi AC Remote Control Not Working
If your Mitsubishi AC Remote Controller isn’t responding, try taking out the batteries and putting them in again.
If this doesn’t work, try bringing the controller closer to your AC unit. The controller should be within 10 metres from the AC unit to work. If the controller is still not working, try resetting the AC unit or the controller (these processes will be explained later).
How to Manually Reset a Mitsubishi Air Conditioning System

Sometimes, resetting either your Mitsubishi air conditioner or its remote controller may help solve many of the problems mentioned in our Mitsubishi Air Conditioning Troubleshooting Guide.
How to Reset a Mitsubishi AC Unit
Resetting your Mitsubishi AC Unit may help resolve some minor problems. Here’s how you do it.
First, try resetting the unit with your remote controller. Simply press the reset button located at the bottom of the remote’s control panel.
If this doesn’t work, open your home’s breaker board and turn off the switch connected to the AC. Wait for 30 seconds and then flip the switch on again. It may take the AC a few minutes to get back up to speed, but if it’s still giving you problems, you may need to call a professional.
How to Reset a Mitsubishi Remote Control
If changing the batteries didn’t help make your remote function normally again, try resetting it. Simply keep the power button pressed for a few seconds. The button light will blink twice and then turn off. Your remote is now reset.
Common Mitsubishi AC Error Codes

If your Mitsubishi air conditioner has an issue, it may show an error code on its control panel’s display. Here’s a list of potential error codes and what they mean.
Mitsubishi 4 Digit Error Codes
| Error Code Type | Description |
| 0403 | Serial communication error |
| 0900 | Test run |
| 1102 | Discharge temperature fault |
| 1301 | Low pressure fault |
| 1302 | High pressure fault |
| 1500 | Refrigerant overcharge |
| 2500 | Drain sensor submergence |
| 2502 | Drain pump fault |
| 2503 | Drain sensor fault |
| 2600 | Water leak |
| 4102 | Open phase |
| 4106 | Transmission power supply fault |
| 4115 | Power supply signal sync error |
| 4116 | RPM error/Motor error |
| 4220 | Abnormal bus voltage |
| 4225 | Low bus voltage |
| 4230/4260 | Heatsink overheat protection activated |
| 4240 | Overload protection activated |
| 4250 | Overcurrent protection activated |
| 4255 | Outdoor unit fan error |
| 5101 | Temperature sensor fault |
| 5102 | Return air thermistor fault |
| 5110 | Outdoor unit inverter heatsink thermistor error |
| 5201 | Pressure sensor fault |
| 5301 | Current sensor fault |
| 5701 | Loose float switch |
| 6201 | Remote controller issue |
| 6600 | Address overlap |
| 6601 | Polarity setting error |
| 6602 | Transmission processor hardware error |
| 6603 | Transmission line busy |
| 6606 | Communication fault |
| 6607 | No ACK |
| 6608 | No response |
| 6831/6834 | MA controller signal reception error |
| 6832/6833 | MA controller comms fault |
| 7100 | Total capacity error |
| 7101 | Capacity code setting error |
| 7102 | Wrong number of connected units |
| 7105 | Address setting error |
| 7106 | Attribute setting error |
| 7110 | Signal transmission error |
| 7111 | Remote controller sensor fault |
| 7113 | Function setting error |
| 7117 | Model setting error |
| 7130 | Incompatible unit combination |
Mitsubishi General Air Conditioning Error Codes
| Error Code Type | Description |
| P1 | Intake sensor error |
| P2 P9 | Pipe (Liquid or 2-phase pipe) sensor error |
| E6 E7 | Indoor/outdoor unit communication error |
| P4 | Drain sensor error |
| P5 | Drain pump error |
| PA | Forced compressor error |
| P6 | Freezing/Overheating safeguard operation |
| EE | Communication error between indoor and outdoor units |
| P8 | Pipe temperature error |
| E4 | Remote controller signal receiving error |
| Fb | Indoor unit control system error (memory error, etc.) |
| E0 E3 | Remote controller transmission error |
| E1 E2 | Remote controller control board error |
| E9 | Indoor/outdoor unit communication error (Transmitting error) (Outdoor unit) |
| UP | Compressor overcurrent interruption |
| U3, U4 | Open/short of outdoor unit thermistors |
| UF | Compressor overcurrent interruption (When compressor locked) |
| U2 | Abnormal high discharging temperature/49C worked/insufficient refrigerant |
| U1 Ud | Abnormal high pressure (63H worked)/Overheating safeguard operation |
| U5 | Abnormal temperature of heat sink |
| U8 | Outdoor unit fan safeguard stop |
| U6 | Compressor overcurrent interruption/Abnormal of power module |
| U7 | Abnormality of superheat due to low discharge temperature |
| U9 | UH Abnormality such as overvoltage or voltage shortage and abnormal synchronous signal to main circuit/ Current sensor error. |
Mitsubishi Mr. Slim A-Control Error Codes
| Error Code Type | Description |
| EA | Error detail Miswiring of indoor/outdoor unit. exceed the number of indoor unit connection. |
| EB | Error detail Miswiring of indoor/outdoor unit. (mis-wiring disconnection) |
| EC | Error detail Start-up time over |
| E6 | Error detail Indoor/outdoor unit transmission error (signal receiving error) |
| E7 | Error detail Indoor/outdoor unit transmission error (transmitting error) |
| E8 | Error detail Indoor/outdoor unit transmission error (signal receiving error) |
| E9 | Error detail Indoor/outdoor unit transmission error (transmitting error) |
| E0 | Error detail Remote control transmission error (signal receiving error) |
| E3 | Error detail Remote control transmission error (transmitting error) |
| E4 | Error detail Remote control transmission error (signal receiving error) |
| E5 | Error detail Remote control transmission error (transmitting error) |
| EF | Error detail M-NET transmission error |
| ED | Error detail Serial transmission error |
| P1 | Error detail Abnormality of room temperature thermistor (TH1) |
| P2 | Error detail Abnormality of pipe temperature thermistor/liquid (TH2) |
| P4 | Error detail Abnormality of drain sensor (DS) |
| P5 | Error detail Malfunction of drain-up machine |
| P6 | Error detail Freezing/overheating protection detect |
| P8 | Error detail Abnormality of pipe temperature |
| P9 | Error detail Anormality of pipe temperature thermistor/condenser/evaporator (TH5) |
| F1 | Error detail Reverse phase detection |
| F2 | Error detail L3 open phase detection |
| F3 | Error detail 63L connector open |
| F4 | Error detail 49C connector open |
| F9 | Error detail Connector 2 or more open |
| FA | Error detail L2-phased open phase or 51CM connector open |
| F7 | Error detail Reverse phase detection circuit (p.c.board) fault |
| F8 | Error detail Input circuit fault |
| U2 | Error detail Abnormal high discharging temperature |
| U2 | Error detail Inner thermostat (49C) operation |
| U1 | Error detail Abnormal high pressure (high pressure swicth 63H worked) |
| U1 | Error detail Direct cut operation |
| UE | Error detail High pressure error (ball valve closed) |
| UL | Error detail Abnormal low pressure |
| UD | Error detail Overheat protection |
| U6 | Error detail Compressor over current (overload) cut off |
| UA | Error detail Compressor over current (terminal relay operation) |
| UF | Error detail Compressor over current (start-up locked) cut off |
| UF | Error detail Compressor over current (operating locked) cut off |
| UH | Error detail Current sensor error |
| U3 | Error detail Discharge thermistor short/open |
| U4 | Error detail Outdoor thermistor short/open |
| Mr.Slim K-control | Display of remote controller |
| LED E0 | Diagnosis of malfunction Transmitting/receiving signal error |
| LED P1 | Diagnosis of malfunction Intake air sensor abnormal |
| LED P2 | Diagnosis of malfunction Pipe sensor abnormal |
| LED P4 | Diagnosis of malfunction Drain sensor abnormal |
| LED P5 | Diagnosis of malfunction Malfunctioning of the drain overflow protecting mechanism |
| LED P6 | Diagnosis of malfunction Abnormality of the coil frost/overheating protection mode |
| LED P3 | Diagnosis of malfunction System error (transmitting/receiving signal) |
| LED P7 | Diagnosis of malfunction System error (address) |
| LED P8 | Diagnosis of malfunction Outdoor unit malfunction |
| Mr.Slim K-control | PUH-EK Outdoor unit |
| LED ON | Operation status |
| LED Flash | Check code display |
| LED LD1 | LED ON Compressor directive
LED Flash Reverse phase detect |
| LED LD2 | LED ON Heating directive
LED Flash Open phase detect |
| LED LD3 | LED ON During 63H1 operation
LED Flash Pipe sensor short/open |
| LED LD4 | LED ON Compressor ON
LED Flash High pressure switch (63H2) operation |
| LED LD5 | LED ON Outdoor fan ON
LED Flash Over current relay (51CM) operation |
| LED LD6 | LED ON 4-way valve ON
LED Flash Thermal switch (26C) operation |
| LED LD7 | LED ON Bypass valve ON
LED Flash Thermistor (TH3) overheat protection |
| LED LD8 | LED ON Crankcase heater ON
LED Flash Defective input |
Mitsubishi Mr. Slim Error Codes (For Membrane Remote Controllers)
| Error Code Type | Description |
| EO | During individual unit control:
Bad contact of transmission wire Signal transmitting/receiving circuits are abnormal |
| P1 | Bad contact of thermistor
Damaged thermistor |
| P2 | Bad contact of thermistor
Damaged thermistor |
| P3 | Bad contact of transmission wire
Signal transmitting/receiving circuits are abnormal Wrong operation due to noise wave emitted by other appliances |
| P4 | Bad contact of transmission wire
Damaged thermistor |
| P5 | Malfunction of drain pump
Damaged drain sensor |
| P6 | Short cycle of air cycle
Dirty air filter Damaged fan Abnormal refrigerant |
| P7 | Wrong address-setting
Signal transmitting/receiving circuit of remote controller is abnormal Wrong SW6-setting |
| P8 | Wrong wiring of indoor/outdoor connecting wire
Reversed phase Protection device is working Damaged outdoor coil thermistor |
Download the Mitsubishi Manual for Your AC Unit
If our Mitsubishi AC Troubleshooting Guide did not help you resolve your problem or your problem relates to a specific model then this manufacturer’s manual from Mitsubishi may have what you’re looking for.
When to Call a Professional for Mitsubishi Air Conditioning Repair
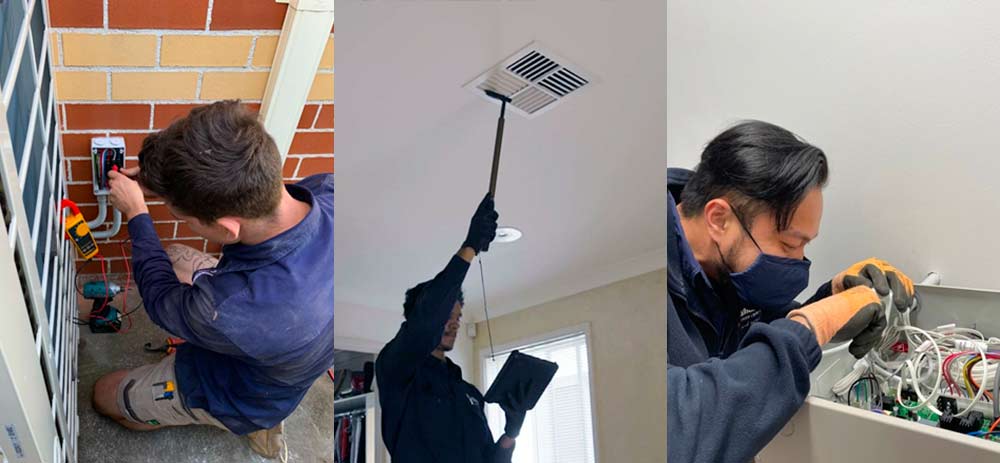

If you’re not too confident about resolving a problem you have with your Mitsubishi air conditioner by yourself, there are issues with your unit that persist, or you see any of the error codes mentioned above, you may need to call a professional to come and repair your air conditioner.
Air Conditioning Repair vs Replacement
If your AC is frequently having problems, it’s over 15 years old, or your Mitsubishi Air Conditioner not turning on is a problem that continues, you may want to consider an replacing your air conditioner altogether.
An old system is likely to be plagued with more difficulties as it depreciates and sourcing replacement parts can also become extremely costly and time consuming. Luckily, at Alliance Climate Control, we’re offering a sustainable replacement discount over the cold winter months so you can keep your indoor temperature in check.
Call Now and Save Up To $1200 with our Exclusive Online Trade-In Offer

Up to
With any aircon replacement trade in*
*Offer to be presented at point of booking or sale. Not to be combined with any other offer.
Up to
With any new Air conditioning supply and installation*
*Offer to be presented at point of booking or sale. Not to be combined with any other offer.

Up to
With any new central
gas heater supply and install*
*Offer to be presented at point of booking or sale. Not to be combined with any other offer.
system

Up to
With any air con or gas heater replacement trade in*
*Offer to be presented at point of booking or sale. Not to be combined with any other offer.
Installation

Up to
With any new Air conditioning
supply and installation*
*Offer to be presented at point of booking or sale. Not to be combined with any other offer.
Schedule an appointment with
one of our specialists today.
Qualified Mitsubishi Air Conditioner Repairs and Replacement
If you’re looking for qualified Mitsubishi Air Conditioning replacement or repair, Alliance Climate Control is here to help! We have 15 years of experience in providing customers in NSW with the highest-quality cooling and heating solutions – give us a call today!

